Industry 4.0
Moving forward together: Industry 4.0 working groups
In Germany and throughout the world

National working groups
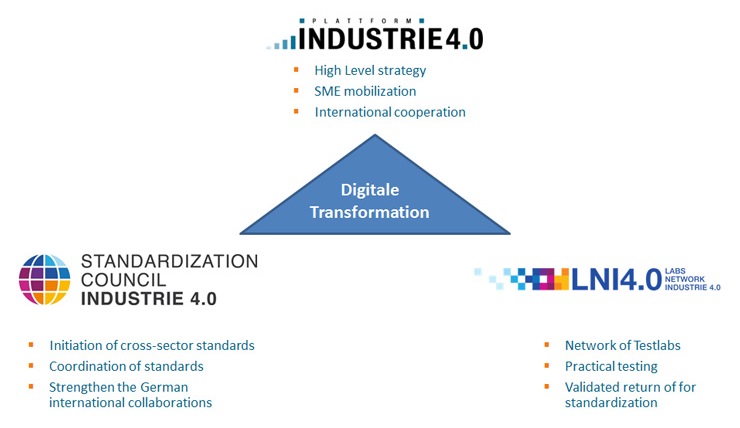
Plattform Industrie 4.0 was created in 2013 by the three industrial associations BITKOM, VDMA and ZVEI and is currently under the leadership of the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi) and the Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF). Plattform Industrie 4.0 brings together representatives from the business sector, the scientific sector, trade unions, politics and consumer groups, in order to work towards achieving a shared future for Germany as an industrial location. In terms of subject matter, it focusses on the fields of research and innovation, the security of networked systems, legal frameworks, work, and further education and training. Of course, this is all in addition to standardization. DIN is involved in these working groups and is supporting Plattform Industrie 4.0 in applying their outcomes to the process of standardization, especially on an international level.
Standardization Council Industrie 4.0
Together with the industrial associations BITKOM, VDMA and ZVEI, DIN and DKE founded the Standardization Council Industrie 4.0 (SCI 4.0). The SCI 4.0 is responsible for orchestrating standardization activities and, in this role, acts as a point of contact in connection with all matters relating to standardization in the context of Industrie 4.0. In collaboration with the Plattform Industrie 4.0, the SCI 4.0 brings German stakeholders together and represents their interests in international bodies and consortia. SCI 4.0 is also supporting the concept of practical testing in test centres, by initiating and carrying out new standardization projects that fulfil the needs that have been identified.
The SCI 4.0 panel of experts is also responsible for the creation and publication of the Standardization Roadmap for Industrie 4.0. The Roadmap is continually being updated and you can find the latest version here.
The Labs Network Industrie 4.0 (LNI 4.0) was set up by companies from the Plattform Industrie 4.0, together with BITKOM, VDMA and ZVEI. In the test centres, new technologies, business models and use cases in Industrie 4.0 can be tested and their technical and economic feasibility be examined before they are launched on the market. This means that LNI 4.0 offers an ideal laboratory and experimental environment, particularly for small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs). Thanks to close collaboration with the SCI 4.0 and DIN, new Industrie 4.0 solutions, and the standards and technical rules they draw on, can be tested. In turn, the results flow directly into the further development of standards and technical rules – nationally and internationally.
The interaction of the three organizations forms a quick-reacting and interwoven structure of strategy, conception, testing and standardization. The collaboration between the partners in the various test centres makes it possible to generate market-relevant requirements. Validated outcomes are then incorporated directly into the standardization process via SCI 4.0. The findings and concepts defined by Plattform Industrie 4.0 are also taken into account and carried across into international standardization in a suitable focused manner via SCI 4.0.
Working groups at DIN
Industrie 4.0 topics are handled by various committees at DIN. These include, among others:
- IT Security Coordination Office (KITS)
- DIN Standards Committee Services (NADL)
- DIN Standards Committee Mechanical Engineering (NAM)
- DIN Standards Committee technology of materials (NWT)
- DIN Standards Committee Machine Tools (NWM)
- DIN Standards Committee Tools and Clamping Devices (FWS)
- DIN Standards Committee Safety Design Principles (NASG)
- DIN Standards Committee Information Technology and selected IT Applications (NIA)
- DIN Standards Committee Ergonomics (NAErg)
- DIN Standards Committee Technical Fundamentals (NATG)
The work results from these committees all flow into the SCI 4.0.
International working groups
Working groups are also involved with standards and technical rules on an international level. The results flow back into the national activities. Of particular importance is the work of:
ISO/TC 184 Automation systems and integration
IEC/TC 65 Industrial-process, measurement, control and automation
ISO/IEC JTC 1 Information technology
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42 Artificial Intelligence
ISO/TC 307 Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies
ISO/TMBG/SMCC Smart Manufacturing Coordinating Committee
The ISO Strategic Advisory Group on Industry 4.0 successfully completed its activities in September 2016. The ISO/SMCC was then founded as the replacement committee, with the goal of carrying on the international activities. It is in place for the next two years and is comprised of representatives of the relevant technical committees. Altogether, representatives from 21 ISO committees were nominated for participation, as well as one representative each from the IEC and ITU. Since this began, the ISO/SMCC has been driving the international activities surrounding Industrie 4.0 forward, under German leadership. The goal is to coordinate the work in an interdisciplinary manner and to develop implementation recommendations, in particular with regard to generating a common international approach. At the same time, a national mirror committee was set up at DIN as a means of offering interested parties a national platform that would enable them to take part in the shaping of the work being undertaken on an international level.
IEC/SyC System Committee Smart Manufacturing
The IEC Standardization Evaluation Group Smart Manufacturing (IEC/SEG 7) was entasked with developing a concept for smart manufacturing that spans all relevant areas and bundles them together. This was completed in 2017 and a suggestion was developed for the mandate of the IEC Systems Committee Smart Manufacturing (IEC/SyC) that is to be newly set up. The IEC/SyC is intended to be placed directly beneath the Standardization Management Board (SMB) of the IEC and is expected to take up its work during the second quarter of 2018. Alongside coordinating standardization activities, the tasks of the IEC/SyC are to identify gaps and overlaps, especially relating to the collaboration between relevant standards organizations and standards-developing organizations (SDOs).
ISO/SMCC – IEC/SEG 7 Task Force Smart Manufacturing Standards Map
This ISO/IEC group was set up by ISO/SMCC and IEC/SEG 7 as a joint working group. Its aim is to draw up, publish and update a body consisting of all Industrie 4.0 standards that is as complete, as dynamic and as simple to manage as possible.
ISO/IEC/JWG 21 Smart Manufacturing Reference Model(s)
Due to the substantive overlaps that exist within the work of ISO/TC 184 and IEC/TC 65, the two bodies formed the Joint Working Group 21 (JWG 21) “Smart Manufacturing Reference Model(s)” in July 2017, in which more than 70 experts from 13 countries take part. Germany and Japan jointly lead the JWG 21. The aim is to bring about the harmonization of existing reference models and to develop Smart Manufacturing reference models, especially with regard to various aspects such as life cycles and the technical and/or organizational hierarchies relating to assets. Furthermore, the development of a fundamental architecture for Smart Manufacturing components as an essential part of the virtual representation of assets is planned (Industrie 4.0 components). The contributions from the various countries are being consolidated, further developed and published in the form of unified and consistent models.